Swelling After Hair Transplant: Normal Versus Concerning Signs
Published on Wed Jan 14 2026
Blog Summary:
Facing swelling after your hair transplant can be a little alarming, but I promise you’re in good company. Swelling, or edema, usually tags along with healing and although it can change your appearance temporarily, it almost never signals trouble. I’ve put together this guide to explain why it shows up, how long you’ll probably notice it, simple steps to ease it, and the signs that mean a call to your doctor is a good idea.
The clearer you are about swelling and its part in your recovery, the less it pulls your attention away from the progress you’re making.
Introduction
Swelling is nothing more than your body’s way of taking care of itself. During a hair transplant, the tiny cuts made for the grafts create mild trauma in your scalp. That trauma sparks inflammation, the body’s built-in repair signal. An extra rush of fluid often tags along with inflammation, giving you the firm, tight feeling you may notice.
The puffiness can reach beyond your scalp. Fluid may move down to your forehead, and, in some cases, a slight heaviness can settle around the eyes. Gravity is the reason it drifts downward, and even the worst-looking puffiness is still textbook normal. If you only picture a neat recovery, it can be a little alarming to see it.
Take this for comfort: swelling is proof that your body is working, not something going sideways. It’s the exact, wise reply your body gives when it’s fixing itself.
Understanding Normal Swelling
Swelling after a hair transplant is a natural reaction. It happens because of the surgery itself and the fluids used during the procedure. It is a normal part of the healing process and usually nothing to worry about.
Causes of Normal Swelling
- Anesthesia and Saline Solution: During the procedure, doctors inject local anesthesia and a saline solution into the scalp. This numbs the area and helps make the skin firmer, which makes it easier to take out and place the hair grafts. This fluid can build up in the tissues, leading to swelling.
- Inflammation: When new hair sites are created and grafts are taken, it causes a small amount of tissue injury. This triggers an inflammatory response. This inflammation increases blood flow and causes fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues, which contributes to the swelling.
- Gravity: Swelling often moves downwards due to gravity. As fluids gather in the scalp, they tend to move towards the face, often affecting the forehead, eyelids, and sometimes even the nose or cheeks.
Typical Timeline of Normal Swelling
Normal swelling usually follows a clear pattern:
- Day 1 to 2: Swelling typically starts on the second day after the procedure. It might be slight at first and mostly on the forehead.
- Day 3 to 4: Swelling usually reaches its peak around the third or fourth day after surgery. During this time, it can be most noticeable, extending to the eyelids and sometimes making it hard to open the eyes temporarily.
- Day 5 to 7: After its peak, the swelling slowly starts to go down. By the end of the first week, most of the visible swelling, especially on the face, should have greatly reduced or disappeared completely.
- Beyond 7 Days: While the swelling on the face usually goes away within a week, some minor swelling on the scalp might stay for a longer time, sometimes up to two or three weeks. This is often less noticeable and will resolve on its own.
Characteristics of Normal Swelling
Normal swelling typically has these features:
- Soft and Pitting: If you gently press the swollen area, it might leave a temporary dent. This shows that fluid has built up.
- Not Painful or Mildly Uncomfortable: The area might feel tight or a little uncomfortable, but normal swelling usually does not cause severe pain. Any discomfort can typically be managed with common pain relievers.
- Often Symmetrical: Swelling tends to be fairly even on both sides of the face or forehead.
- Resolves on Its Own: The most important sign of normal swelling is that it gradually disappears within the expected timeframe, either without any special treatment or with simple care.
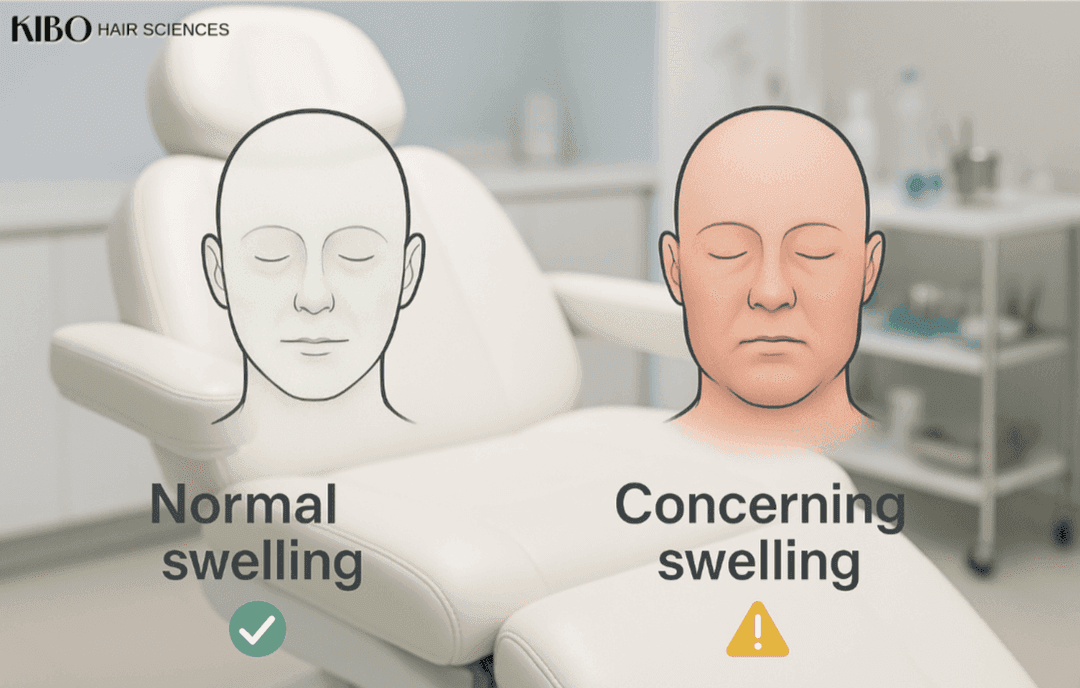
Identifying Concerning Signs of Swelling
While some swelling is normal, certain signs can point to a possible problem, like an infection or a bad reaction. It is very important for patients to know these warning signs and to contact their clinic right away if they notice any of the following:
1. Swelling That Stays or Gets Worse Beyond the Expected Time
If swelling does not start to go down after day 4 or 5, or if it keeps getting worse after the first week, it could mean that there is an issue. Normal swelling should slowly decrease and go away within 7 to 10 days. Swelling that lasts too long or gets bigger might mean there is fluid build up also called seroma or an inflammatory process that needs to be checked by a doctor.
2. Severe Pain or Tenderness
Some mild discomfort is normal, but severe, throbbing, or increasing pain that pain medication does not help is a worrying sign. This could mean an infection, inflammation, or other problems that need immediate attention.
3. Redness, Warmth, or Pus Coming Out
If the transplanted area is red and warm, especially if there is pus or any other fluid coming out, these are clear signs of infection. Infections are rare, but they can harm the transplanted hair and overall healing. Any bad smell from the scalp is also a serious warning sign.
4. Fever or Chills
Feeling generally unwell with a fever (temperature above 100.4°F or 38°C) and chills can mean a general infection or a strong inflammatory reaction that needs quick medical review. These symptoms, especially when seen with local signs, mean you should talk to a doctor right away.
5. Swelling on Only One Side or Uneven Swelling
While normal swelling can sometimes be a little uneven, significant swelling that is only on one side of the face or scalp, or that looks very lopsided, could mean a local problem. This might be a hematoma (a collection of blood) or an infection.
6. Numbness or Tingling That Gets Worse or Lasts Too Long
Some temporary numbness in the areas where hair was taken or placed is common because of nerve changes during surgery. However, if numbness gets worse, spreads, or lasts for an unusually long time (more than a few weeks), you should tell the clinic. This could point to nerve damage or pressure.
7. Blisters or Skin Changes
Any signs of blisters, changes in skin color (beyond normal redness), or changes in skin texture in the transplanted area or nearby should be reported immediately. These could mean a severe inflammatory reaction, an allergic reaction, or, in very rare cases, a problem with blood flow.
Knowing these concerning signs is very important for getting help quickly and making sure your hair transplant has the best possible outcome. If you are ever unsure, it is always best to be safe and contact your hair transplant specialist.
Management of Swelling
Most swelling after a hair transplant will go away on its own. However, there are several good ways to help reduce how much swelling you have, make you more comfortable, and help it disappear faster. Hair transplant specialists usually suggest these management techniques as part of your care instructions after the procedure.
1. Keeping Your Head Up
Keeping your head elevated, especially for the first three to five nights after the procedure, is one of the most important steps to prevent and reduce swelling. Sleeping with your head raised at about a 45 degree angle (you can use two or three pillows, or a recliner chair) helps gravity move the extra fluids away from your face and scalp. This simple action can significantly lessen how much your face swells.
2. Using Cold Packs
Putting cold packs on your forehead and around your eyes can help tighten blood vessels, reduce inflammation, and ease swelling. It is important to only put cold packs on your forehead and temples. Do not put them directly on the transplanted area, as this could move the newly placed hair grafts. You can use cold packs for 15 to 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, during the first two to three days after surgery.
3. Staying Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for healing and helps your body get rid of extra fluids. Even though it might seem strange, staying well hydrated helps your kidneys work properly and naturally removes swelling.
4. Medications
- Anti inflammatory Medications: Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and pain. Always follow your surgeon's specific instructions for using them, as some might thin your blood.
- Steroids: Sometimes, a short course of oral corticosteroids might be prescribed to greatly reduce swelling, especially for patients who tend to have more noticeable swelling. These are usually given for a few days right after the procedure.
- Diuretics: In rare cases, if swelling is severe and does not go away, a mild diuretic might be considered. However, this is usually done under strict medical supervision and is not a common recommendation.
5. Avoiding Strenuous Activities
For the first week to ten days, it is best to avoid hard physical activities, heavy lifting, and exercises that increase blood pressure in your head. Such activities can make swelling worse and might harm the healing of the transplanted hair grafts. Light walking is usually fine and can even help with blood flow.
6. Limiting Salt Intake
Eating less salt for the first few days after the procedure can help reduce fluid retention in your body, which might lessen swelling. Choose fresh, unprocessed foods and avoid salty snacks.
7. Gentle Scalp Care
Follow your surgeon's instructions for gently washing your scalp. Regular, gentle washing helps remove scabs and crusts, which can sometimes add to local swelling and discomfort. Make sure the water pressure is low and avoid rubbing or scrubbing the transplanted area.
By carefully following these management tips, patients can effectively control swelling after a hair transplant. This leads to a more comfortable recovery and helps achieve the best possible results.
Prevention of Swelling
While it is almost impossible to completely stop some swelling after a hair transplant, there are many things you can do to greatly reduce how likely it is to happen and how severe it will be. Hair transplant clinics often include these preventive steps in their instructions before and after surgery.
1. Medications Before Surgery
Some clinics might give you a short course of oral corticosteroids (like Prednisone) to start a day or two before surgery and continue for a few days afterwards. These medicines are strong anti inflammatory agents that can effectively reduce inflammation and the swelling that follows. However, your surgeon will decide if you should use them based on your health history and how much surgery you are having.
2. Correct Anesthesia Method
The way local anesthesia is given can affect how much fluid builds up. Experienced surgeons use careful methods to inject just the right amount of fluid. This helps avoid too much fluid that could cause more noticeable swelling.
3. Keeping Your Head Up After Surgery
As mentioned in the management section, keeping your head elevated is not just a way to treat swelling, but also a very important way to prevent it. By keeping your head raised at a 45 degree angle, especially when you sleep, gravity helps drain fluids away from your face and scalp. This stops them from collecting and causing a lot of swelling. You should start doing this right after the procedure.
4. Avoiding Strenuous Activities and Head Injuries
Right after surgery, it is very important to avoid any activities that increase blood pressure in your head. This includes heavy lifting, intense exercise, or bending over. These actions can make swelling worse by increasing fluid pressure in the surgical area. It is also essential to protect your head from any bumps or injuries, as these can cause more inflammation and swelling.
5. Limiting Salt and Alcohol
Eating too much salt and drinking alcohol can both cause your body to hold onto more fluid. It is a good idea to limit salty foods and avoid alcohol for at least a few days before and after surgery. This can help reduce overall fluid retention in your body, which then lowers the chance of swelling in your scalp and face.
6. Using a Headband or Compression Bandage
Some surgeons suggest wearing a soft compression headband or bandage around your forehead for the first few days after the procedure. This gentle pressure can help guide any fluid away from your face and down towards your neck, where your body can absorb it more easily. It acts as a physical barrier to stop swelling from moving to your eyelids and forehead.
By using these preventive steps along with careful post operative care, patients can significantly reduce how much swelling they experience and how long it lasts. This leads to a more comfortable and smoother recovery after a hair transplant.
Expected Results and Longevity
One of the most common questions patients have is about how long a hair transplant lasts. The results of a well performed hair transplant are considered permanent. This is because the transplanted hair follicles are taken from the donor area (usually the back and sides of the head), which is naturally resistant to the effects of DHT. DHT is the hormone responsible for male and female pattern baldness. These follicles keep their natural characteristics even after being moved to new areas, meaning they will continue to grow hair for a lifetime.
However, it is important to understand that while the transplanted hair is permanent, the natural hair around the transplant might continue to thin over time. Because of this, a long term treatment plan is often suggested to keep the overall appearance consistent and to prevent further hair loss. This might include medications like finasteride or minoxidil, or other treatments to support the health of the existing hair.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is swelling after a hair transplant normal? A: Yes, mild to moderate swelling is a very common and normal part of the healing process after a hair transplant. It typically starts on day 2 or 3 and resolves within a week.
Q: How can I reduce swelling after my hair transplant? A: You can reduce swelling by keeping your head elevated, especially when sleeping, applying cold compresses to your forehead (avoiding the transplanted area), staying well hydrated, and following any specific medication instructions from your surgeon.
Q: When should I be concerned about swelling? A: You should contact your clinic if swelling is severe, persistent beyond the expected timeline, accompanied by severe pain, redness, warmth, pus, fever, chills, or if it is significantly uneven.
Q: Can swelling affect the transplanted grafts? A: Normal swelling does not typically harm the transplanted grafts. However, severe or prolonged swelling, especially if it is a sign of infection or other complications, could potentially impact graft survival. This is why it is important to follow post operative care instructions and report any concerning signs.
Q: How long does it take for all swelling to go away? A: Most visible facial swelling usually subsides within 7 to 10 days. Any residual swelling on the scalp might take a few more weeks to completely resolve, but it is usually less noticeable.
Why Choose Kibo Hair Sciences Clinic
At Kibo Hair Sciences Clinic, patient care and successful outcomes are the top priorities. The clinic combines advanced hair transplant techniques with a patient centered approach, ensuring a comfortable and effective experience. The team of specialists provides thorough pre operative consultations, meticulous surgical procedures, and comprehensive post operative care, including detailed guidance on managing and preventing swelling. With a focus on natural looking and lasting results, Kibo Hair Sciences Clinic is dedicated to helping individuals regain their confidence through expert hair restoration.
Services
Hair Regrowth Solutions
GFC Therapy | IV Hair Booster | Low-Level Laser Helmet Therapy | Mesotherapy for Hair Regrowth | Microneedling for Hair Regrowth | PDO Threads for Hair Regrowth | PRP Therapy
Hair Transplant Options
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) | Sapphire FUE | Body Hair Transplant | Corrective Hair Transplant | Hairline Correction | Unshaven Hair Transplant | Direct Hair Transplant (DHT) | Real Time FUE | Bio FUE
Related Blogs
Self-Care Routines in the First Week | What to Do Before and After Transplant Week | Returning to Gym and Outdoor Activities | Dealing with the Ugly Duckling Phase | Shock Loss After a Hair Transplant | Uneven Growth in Early Recovery | Hair Shedding in the First Month | Donor Scar Visibility and Healing | Long-Term Maintenance After Transplant | How Patience Shapes Visible Results